Publications
2024
View Publication
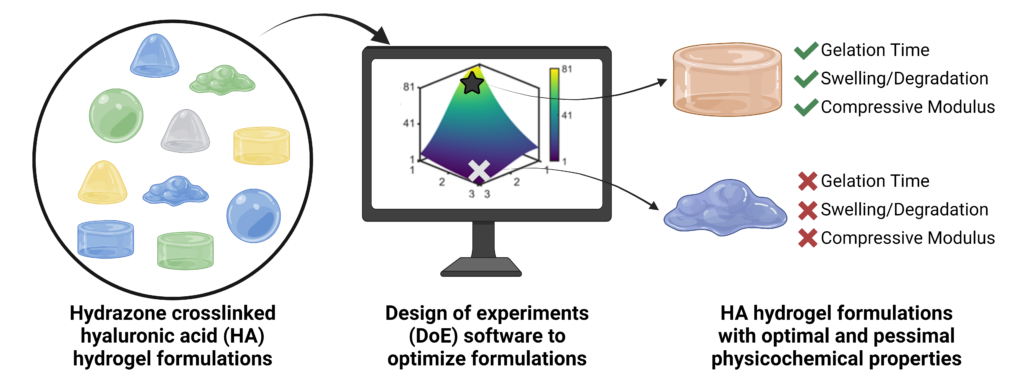
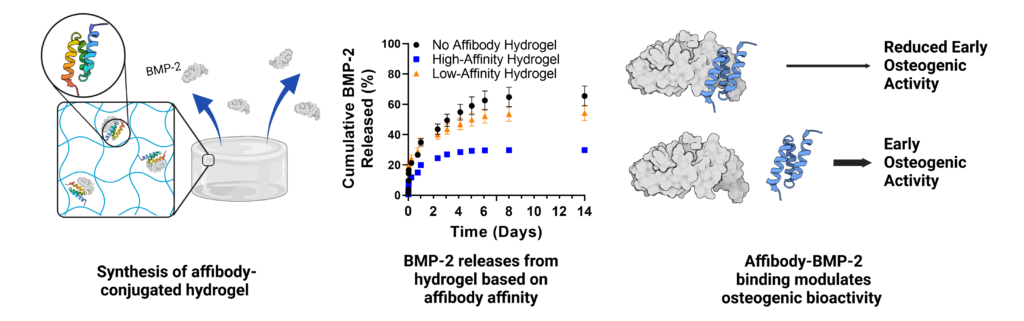
Hydrazone-crosslinked hydrogels are attractive protein delivery vehicles for regenerative medicine. However, each regenerative medicine application requires unique hydrogel properties to achieve an ideal outcome. The properties of a hydrogel can be impacted by numerous factors involved in its fabrication. We used design of experiments (DoE) statistical modeling to efficiently optimize the physicochemical properties of a hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrazone-crosslinked hydrogel for protein delivery for bone regeneration. We modified HA with either adipic acid dihydrazide (HA-ADH) or aldehyde (HA-Ox) functional groups and used DoE to evaluate the interactions of three input variables, the molecular weight of HA (40 or 100 kDa), the concentration of HA-ADH (1–3% w/v), and the concentration of HA-Ox (1–3% w/v), on three output responses, gelation time, compressive modulus, and hydrogel stability over time. We identified 100 kDa HA-ADH3.00HA-Ox2.33 as an optimal hydrogel that met all of our design criteria, including displaying a gelation time of 3.7 minutes, compressive modulus of 62.1 Pa, and minimal mass change over 28 days. For protein delivery, we conjugated affinity proteins called affibodies that were specific to the osteogenic protein bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) to HA hydrogels and demonstrated that our platform could control the release of BMP-2 over 28 days. Ultimately, our approach demonstrates the utility of DoE for optimizing hydrazone-crosslinked HA hydrogels for protein delivery.
2023
View Publication
Uncontrolled bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) release can lead to off-target bone growth and other adverse events. To tackle this challenge, yeast surface display is used to identify unique BMP-2-specific protein binders known as affibodies that bind to BMP-2 with different affinities. Biolayer interferometry reveals an equilibrium dissociation constant of 10.7 nm for the interaction between BMP-2 and high-affinity affibody and 34.8 nm for the interaction between BMP-2 and the low-affinity affibody. The low-affinity affibody-BMP-2 interaction also exhibits an off-rate constant that is an order of magnitude higher. Computational modeling of affibody-BMP-2 binding predicts that the high- and low-affinity affibodies bind to two distinct sites on BMP-2 that function as different cell-receptor binding sites. BMP-2 binding to affibodies reduces expression of the osteogenic marker alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in C2C12 myoblasts. Affibody-conjugated polyethylene glycol-maleimide hydrogels increase uptake of BMP-2 compared to affibody-free hydrogels, and high-affinity hydrogels exhibit lower BMP-2 release into serum compared to low-affinity hydrogels and affibody-free hydrogels over four weeks. Loading BMP-2 into affibody-conjugated hydrogels prolongs ALP activity of C2C12 myoblasts compared to soluble BMP-2. This work demonstrates that affibodies with different affinities can modulate BMP-2 delivery and activity, creating a promising approach for controlling BMP-2 delivery in clinical applications.
2021
View Publication
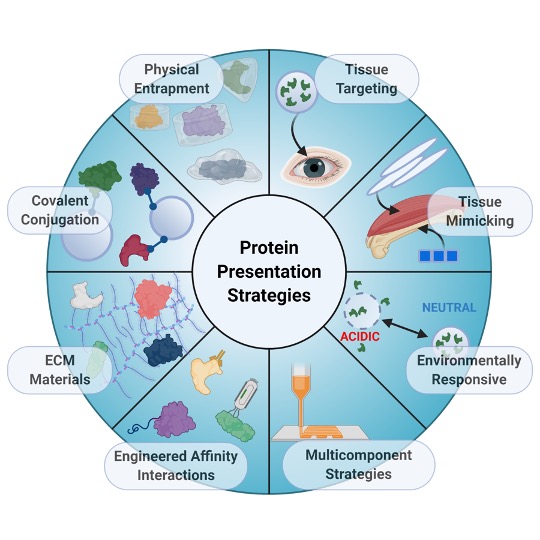
Tissue repair requires a complex cascade of events mediated by a variety of cells, proteins, and matrix molecules; however, the healing cascade can be easily disrupted by numerous factors, resulting in impaired tissue regeneration. Recent advances in biomaterials for tissue regeneration have increased the ability to tailor the delivery of proteins and other biomolecules to injury sites to restore normal healing cascades and stimulate robust tissue repair. In this review, we discuss the evolution of the field toward creating biomaterials that precisely control protein delivery to stimulate tissue regeneration, with a focus on addressing complex and dynamic injury environments. We highlight biomaterials that leverage different mechanisms to deliver and present proteins involved in healing cascades, tissue targeting and mimicking strategies, materials that can be triggered by environmental cues, and integrated strategies that combine multiple biomaterial properties to improve protein delivery. Improvements in biomaterial design to address complex injury environments will expand our understanding of both normal and aberrant tissue repair processes and ultimately provide a better standard of patient care.
View Publication
Type III fractures typically involve segmental bone loss with extensive adjacent soft tissue injury to muscle and vasculature. Such severe composite injuries to bone and muscle often require multiple treatment procedures and are associated with significantly higher rates of complications, including non-union, infection, prolonged disability, and amputation. Successful bone healing depends on early re-vascularization to restore oxygen, nutrient, growth factor, and progenitor cell supply to the injury. Therapeutic angiogenesis strategies have therefore been investigated to promote re-vascularization following severe bone injuries, however results have been inconsistent. In this study, co-stimulation of microvascular fragment constructs with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) promoted vascular network formation in vitro compared to VEGF or PDGF alone. In an in vivo model of segmental bone and volumetric muscle loss injury, combined delivery of VEGF and PDGF with a low dose of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) significantly enhanced regeneration of vascularized bone compared to BMP-2 treatment alone. This study demonstrates the potential for a combined osteoinductive and angiogenic growth factor delivery strategy to promote functional bone regeneration following severe composite musculoskeletal injury.
2020
Press Release: Oregon scientist shows possible path to improved bone-repair procedures
Around the O Story: New Knight Campus bioengineer advances bone repair research
View Publication
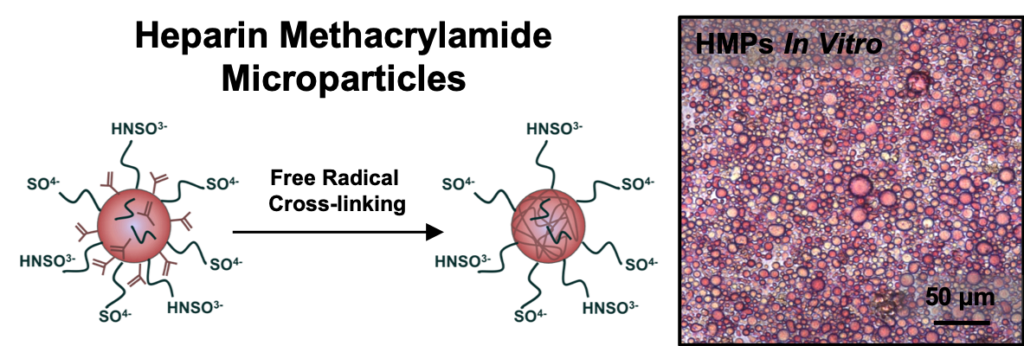
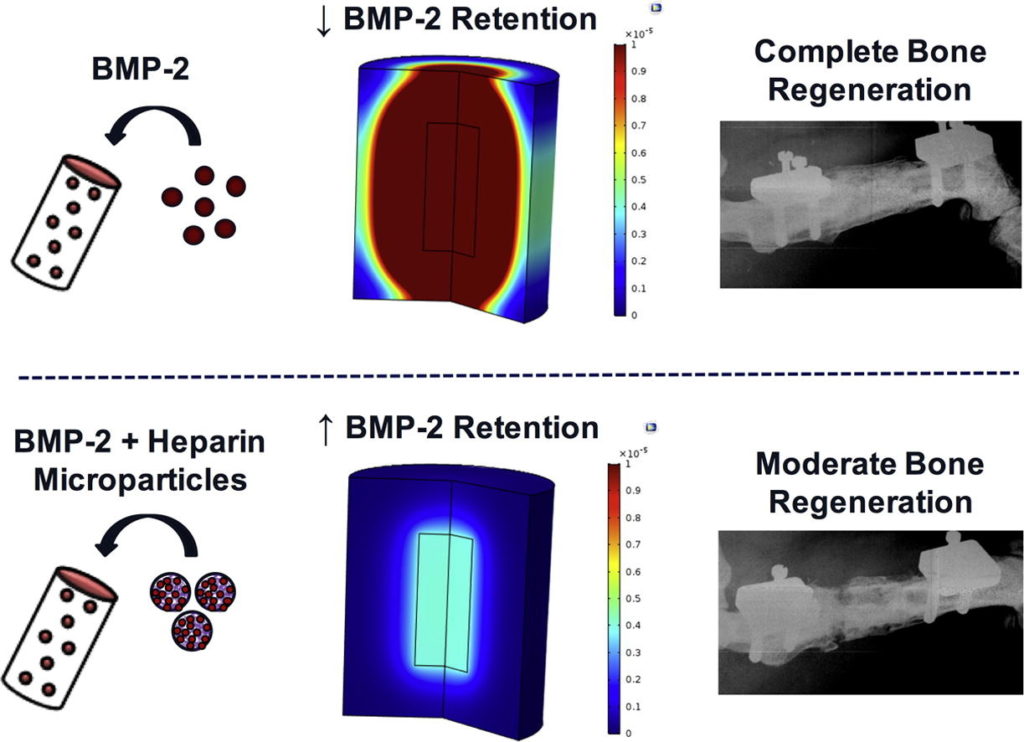
Supraphysiologic doses of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) are used clinically to promote bone formation in fracture nonunions, large bone defects, and spinal fusion. However, abnormal bone formation (i.e., heterotopic ossification) caused by rapid BMP-2 release from conventional collagen sponge scaffolds is a serious complication. We leveraged the strong affinity interactions between heparin microparticles (HMPs) and BMP-2 to improve protein delivery to bone defects. We first developed a computational model to investigate BMP-2–HMP interactions and demonstrated improved in vivo BMP-2 retention using HMPs. We then evaluated BMP-2–loaded HMPs as a treatment strategy for healing critically sized femoral defects in a rat model that displays heterotopic ossification with clinical BMP-2 doses (0.12 mg/kg body weight). HMPs increased BMP-2 retention in vivo, improving spatial localization of bone formation in large bone defects and reducing heterotopic ossification. Thus, HMPs provide a promising opportunity to improve the safety profile of scaffold-based BMP-2 delivery.

Press Release: Re-engineered enzyme could help reverse damage from spinal cord injury and stroke
Around the O Story: Altered enzyme offers hope for spinal injury and stroke
View Publication
Maintaining biocatalyst stability and activity are critical challenges. Chondroitinase ABC (ChABC) has shown promise in central nervous system (CNS) regeneration, yet its therapeutic utility is severely limited by instability. We computationally re-engineered ChABC by introducing between 37 and 92 amino acid changes using consensus design and forcefield-based optimization. All mutants were more stable than wildtype ChABC with increased aggregation temperatures of between 4 and 8 °C. Only ChABC with 37 mutations (ChABC-37) was more active and had a 6.5-times greater half-life than wildtype ChABC, increasing to 106 hours (4.4 days) from only 16.8 hours. ChABC-37, expressed as the fusion protein with Src homology-3 domain (ChABC-37-SH3), was active for 7 days when released from a hydrogel modified with SH3-binding peptides. This study demonstrates the broad opportunity to improve biocatalysts through computational engineering and sets the stage for future testing of this significantly improved protein in the treatment of debilitating CNS injuries.

View Publication
The objective of this study was to investigate the controlled release of two growth factors (BMP-2 and VEGF) as a treatment strategy for clinically challenging composite injuries, consisting of a segmental bone defect and volumetric muscle loss. This is the first investigation of dual growth factor delivery in a composite injury model using an injectable smart delivery system consisting of heparin microparticles and alginate gel. The loading efficiency of growth factors into these biomaterials was found to be >90%, revealing a strong affinity of VEGF and BMP-2 to heparin and alginate. The system could achieve simultaneous or sequential release of VEGF and BMP-2 by varying the loading strategy. Single growth factor delivery (VEGF or BMP-2 alone) significantly enhanced vascular growth in vitro. However, no synergistic effect was observed for dual growth factor (BMP-2 + VEGF) delivery in vitro. Effective bone healing was achieved in all treatment groups (BMP-2, simultaneous or sequential delivery of BMP-2 and VEGF) in the composite injury model. The mechanics of the regenerated bone reached a maximum strength of ~52% of intact bone with sequential delivery of VEGF before BMP-2. Overall, simultaneous or sequential co-delivery of low-dose BMP-2 and VEGF failed to fully restore the mechanics of bone in this injury model. Given the severity of the composite injury, VEGF alone may not be sufficient to establish mature and stable blood vessels when compared with previous studies co-delivering BMP-2+VEGF enhanced bone tissue regeneration. Hence, future studies are warranted to develop an alternative treatment strategy focusing on better control over growth factor dose, spatiotemporal delivery, and additional growth factors to regenerate fully functional bone tissue.
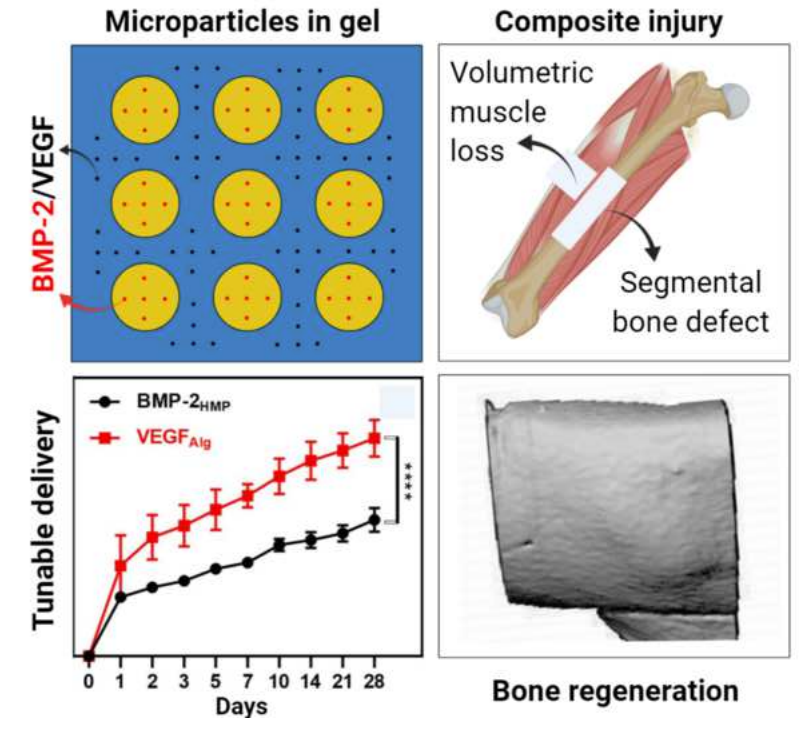
View Publication
A hydrogel that can deliver both proteins and cells enables the local microenvironment of transplanted cells to be manipulated with a single injection. Toward this goal, we designed a hydrogel suitable for the co-delivery of neural stem cells and chondroitinase ABC (ChABC), a potent enzyme that degrades the glial scar that forms after central nervous system (CNS) injury. We leveraged the inverse electron-demand Diels–Alder reaction between norbornene and methylphenyltetrazine to form rapidly gelling (<15 min) crosslinked methylcellulose (MC) hydrogels at physiological temperature and pH, with Young’s modulus similar to that of brain tissue (1–3 kPa), and degradable, disulfide-containing crosslinkers. To achieve tunable, affinity-controlled release of a ChABC-Src homology 3 (SH3) fusion protein, we immobilized norbornene-functionalized SH3-binding peptides onto MC-methylphenyltetrazine and observed release of bioactive ChABC-SH3 over 4 days. We confirmed cytocompatibility by evaluating neural progenitor cell survival and proliferation. The combined encapsulation of neural stem cells and chondroitinase ABC from one hydrogel lays the framework for future in vivo studies to treat CNS injuries.

2019
View Publication
Targeted protein delivery for stimulating tissue repair has been a core focus of the field of tissue engineering for several decades. While many promising protein therapeutics exist, achieving sustained and localized protein delivery to injured tissues remains a challenge. Over the past 25 years, significant breakthroughs have been made in biomaterial-based strategies to improve targeted protein delivery. Protein delivery vehicles that leverage affinity interactions between proteins and materials present an effective approach for modulating the spatiotemporal release of proteins within sites of tissue injury. Stimuli-responsive polymers also enable protein release to be tailored to respond to cell- and tissue-level changes. In this article, we highlight some of the major recent advances in biomaterial strategies for targeted protein delivery with a focus on affinity-based protein delivery systems. We also discuss the future of protein delivery for tissue repair, in which we envision protein delivery strategies that can be tuned in response to the dynamic microenvironment of injured tissues.
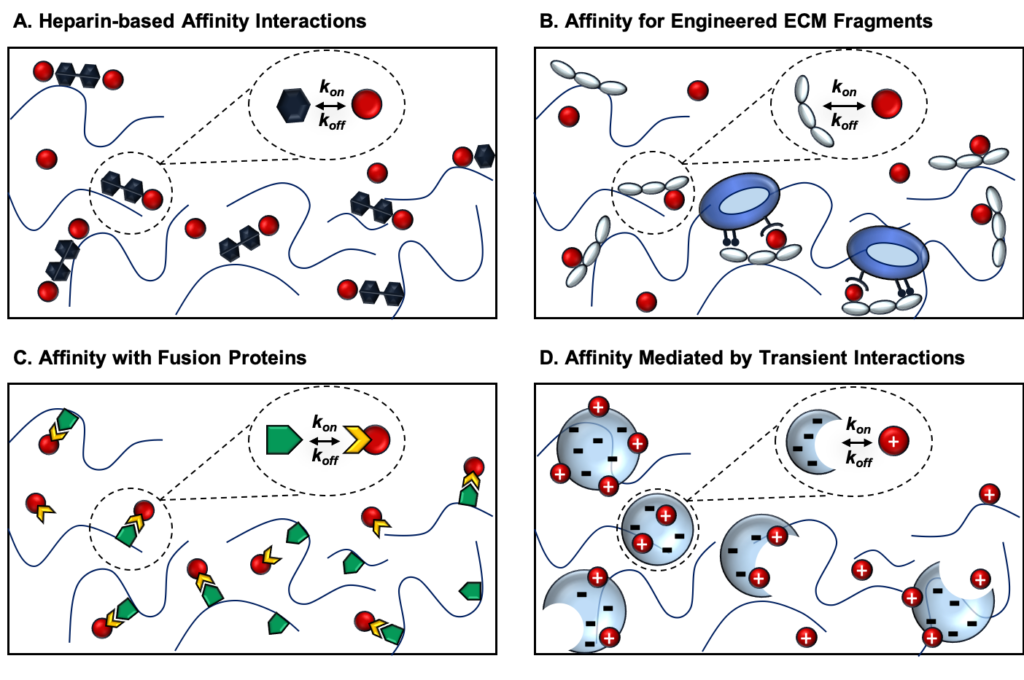
View Publication
Central nervous system (CNS) injuries, such as stroke and spinal cord injury, result in the formation of a proteoglycan-rich glial scar, which acts as a barrier to axonal regrowth and limits the regenerative capacity of the CNS. Chondroitinase ABC (ChABC) is a potent bacterial enzyme that degrades the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG) component of the glial scar and promotes tissue recovery; however, its use is significantly limited by its inherent instability at physiological temperatures. Here, we demonstrate that ChABC can be stabilized using site-directed mutagenesis and covalent modification with poly(ethylene glycol) chains (i.e. PEGylation). Rosetta protein structure modeling was used to screen >20,000 single point mutations, and four potentially stabilizing mutations were tested in vitro. One of the mutations, N1000G (asparagine ➔ glycine at residue 1000), significantly improved the long-term activity of the protein, doubling its functional half-life. PEGylation of this ChABC mutant inhibited unfolding and aggregation and resulted in prolonged bioactivity with a 10-fold increase in activity compared to the unmodified protein after two days. Local, affinity-controlled release of the modified protein (PEG-N1000G-ChABC) was achieved by expressing it as a fusion protein with Src homology 3 (SH3) and delivering the protein from a methylcellulose hydrogel modified with SH3 binding peptides. This affinity-based release strategy provided sustained PEG-N1000G-ChABC-SH3 release over several days in vitro. Direct implantation of the hydrogel delivery vehicle containing stabilized PEG-N1000G-ChABC-SH3 onto the rat brain cortex in a sub-acute model of stroke resulted in significantly reduced CSPG levels in the penumbra of 49% at 14 and 40% at 28 days post-injury compared to animals treated with the vehicle alone.
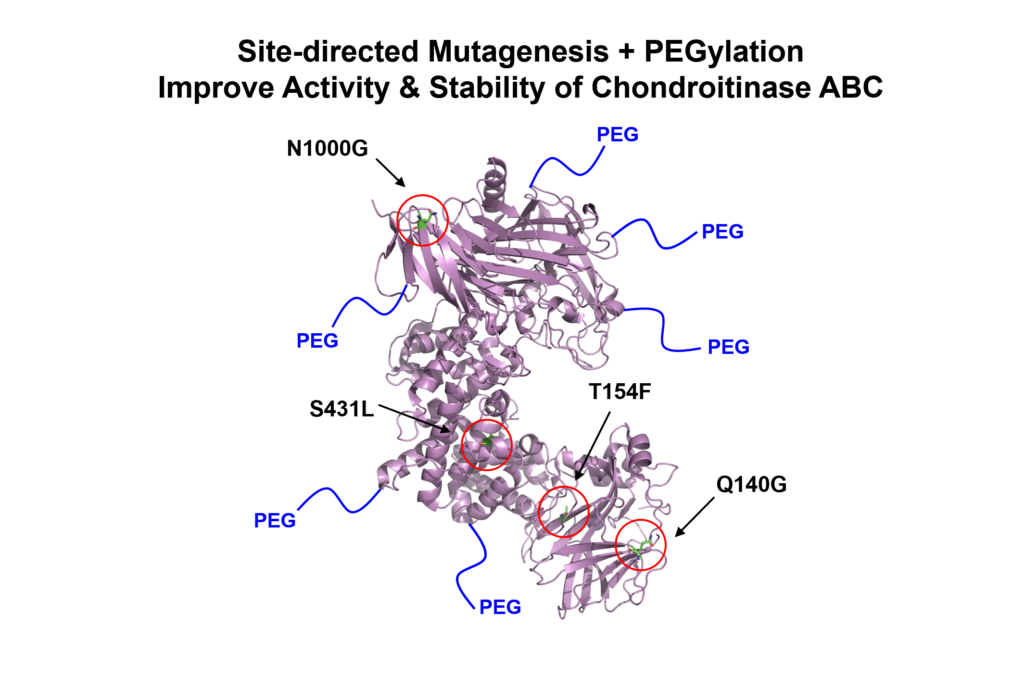
2018
View Publication
Treatment of chronic spinal cord injury (SCI) is challenging due to cell loss, cyst formation, and the glial scar. Previously, we reported on the therapeutic potential of a neural progenitor cell (NPC) and chondroitinase ABC (ChABC) combinatorial therapy for chronic SCI. However, the source of NPCs and delivery system required for ChABC remained barriers to clinical application. Here, we investigated directly reprogrammed human NPCs biased toward an oligodendrogenic fate (oNPCs) in combination with sustained delivery of ChABC using an innovative affinity release strategy in a crosslinked methylcellulose biomaterial for the treatment of chronic SCI in an immunodeficient rat model. This combinatorial therapy increased long-term survival of oNPCs around the lesion epicenter, facilitated greater oligodendrocyte differentiation, remyelination of the spared axons by engrafted oNPCs, enhanced synaptic connectivity with anterior horn cells and neurobehavioral recovery. This combinatorial therapy is a promising strategy to regenerate the chronically injured spinal cord.
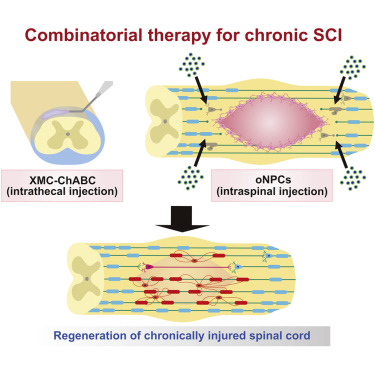
View Publication
Hydrogels present versatile platforms for the encapsulation and delivery of proteins and cells for regenerative medicine applications. However, differences in hydrogel cross-linking density, polymer weight content, and affinity for proteins all contribute to diverse diffusion rates of proteins through hydrogel networks. Here, we describe a simple method to accurately measure protein diffusion through hydrogels, within a few hours and without the use of large amounts of protein. We tracked the diffusion of several proteins of varying molecular weights along the axial direction of capillary tubes filled with alginate, collagen, or poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels. The rate of protein diffusion decreased with increasing molecular weight. A computational model of protein diffusion through capillary tubes was also created to predict and verify experimental protein diffusion coefficients. This in vitro capillary tube-based method of measuring protein diffusion represents a simple strategy to interrogate protein diffusion through natural and synthetic hydrogels and aid in the design of better biomaterial-based delivery vehicles that can effectively modulate protein release.
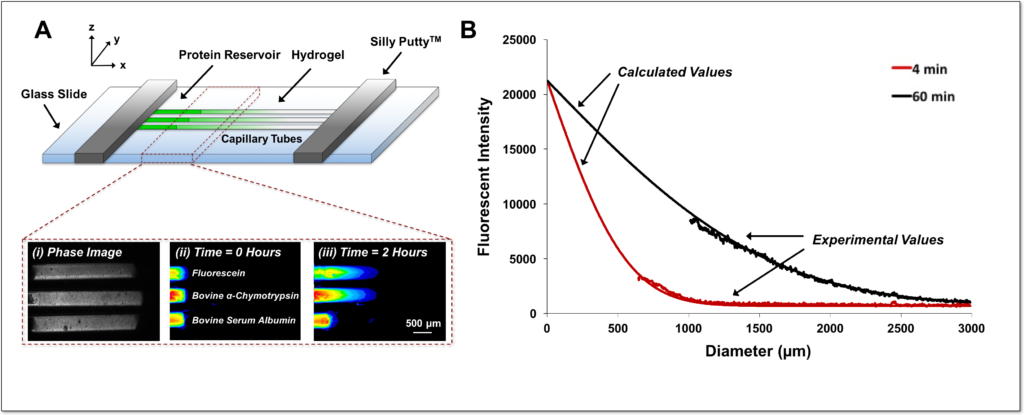
View Publication
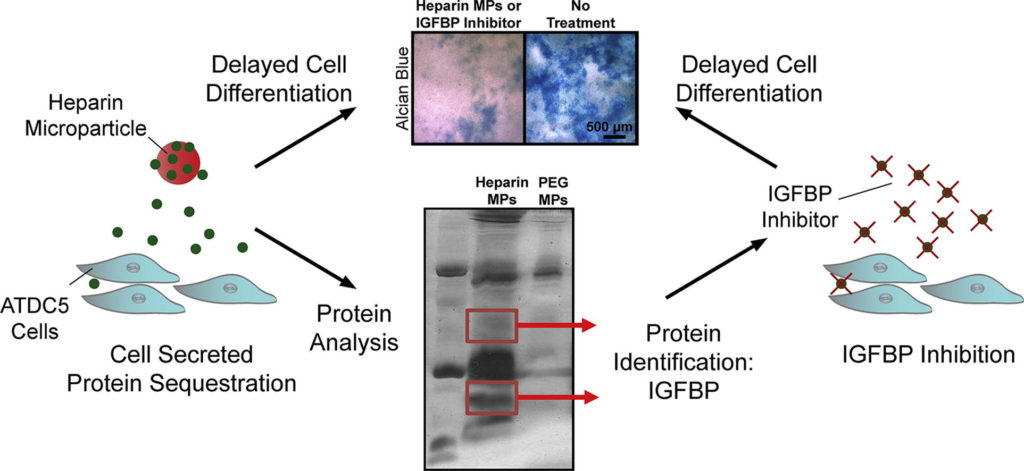
Protein delivery is often used in tissue engineering applications to control differentiation processes, but is limited by protein instability and cost. An alternative approach is to control the cellular microenvironment through biomaterial-mediated sequestration of cell-secreted proteins important to differentiation. Thus, we utilized heparin-based microparticles to modulate cellular differentiation via protein sequestration in an in vitro model system of endochondral ossification. Heparin and poly(ethylene-glycol) (PEG; a low-binding material control)-based microparticles were incorporated into ATDC5 cell spheroids or incubated with ATDC5 cells in transwell culture. Reduced differentiation was observed in the heparin microparticle group as compared to PEG and no microparticle-containing groups. To determine if observed changes were due to sequestration of cell-secreted protein, the proteins sequestered by heparin microparticles were analyzed using SDS-PAGE and mass spectrometry. It was found that heparin microparticles bound insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBP)-3 and 5. When incubated with a small-molecule inhibitor of IGFBPs, NBI 31772, a similar delay in differentiation of ATDC5 cells was observed. These results indicate that heparin microparticles modulated chondrocytic differentiation in this system via sequestration of cell-secreted protein, a technique that could be beneficial in the future as a means to control cellular differentiation processes.
2017
View Publication
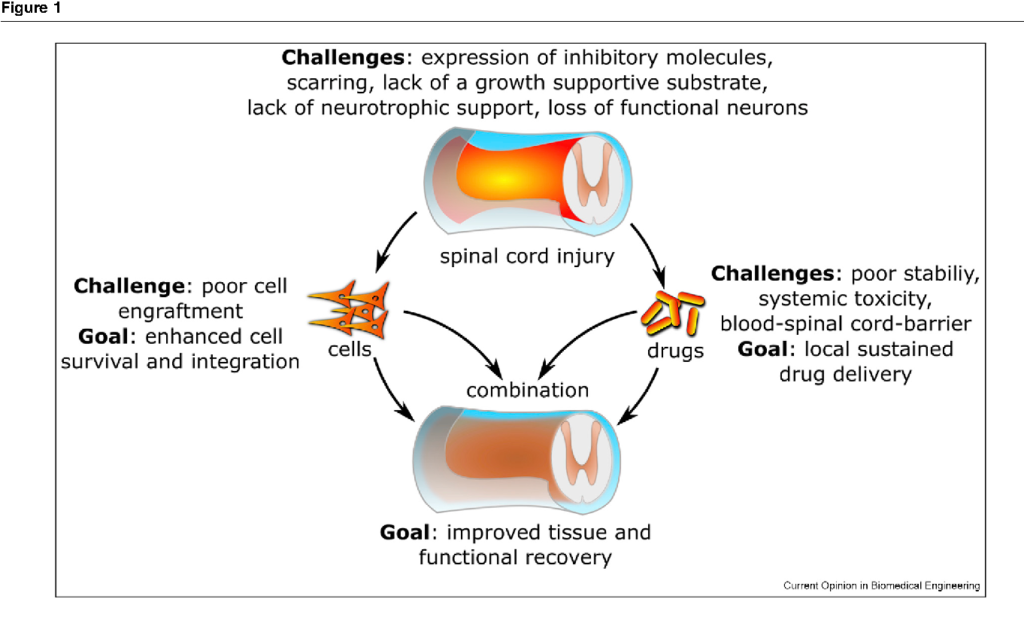
Traumatic injury to the spinal cord leads to a loss of motor and sensory function below the level of injury. The lack of growth-associated proteins, local expression of inhibitory factors, and scar and cyst formation create an inhibitory environment in the spinal cord, which limits the regenerative capacity of endogenous or transplanted cells. Cell and drug delivery strategies, either alone or in combination, can induce changes in the local microenvironment at and around the lesion site to promote transplanted cell survival, integration, and/or endogenous repair. New biomaterial strategies also provide a platform for sustained delivery of otherwise unstable drugs.
View Publication
Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) is an osteoinductive growth factor used clinically to induce bone regeneration and fusion. Some complications associated with BMP-2 treatment have been attributed to rapid release of BMP-2 from conventional collagen scaffolds, motivating the development of tunable sustained-release strategies. We incorporated BMP-2-binding heparin microparticles (HMPs) into a hydrogel scaffold to improve spatiotemporal control of BMP-2 delivery to large bone defects. HMPs pre-loaded with BMP-2 were mixed into alginate hydrogels and compared to hydrogels containing BMP-2 alone. BMP-2 release from scaffolds in vitro, BMP-2 retention within injury sites in vivo, and bone regeneration in a critically sized femoral defect were evaluated. Compared to hydrogel delivery alone, BMP-2-loaded HMPs reduced BMP-2 release in vitro and increased early BMP-2 retention in the bone defect. BMP-2-loaded HMPs induced bone formation at both ectopic and orthotopic sites; however, the volume of induced bone was lower for defects treated with BMP-2-loaded HMPs compared to hydrogel delivery. To better understand the effect of HMPs on BMP-2 release kinetics, a computational model was developed to predict BMP-2 release from constructs in vivo. The model suggested that HMPs limitedBMP-2 release into surrounding tissues, and that changing the HMP density could modulate BMP-2release. Taken together, these experimental and computational results suggest the importance of achieving a balance of BMP-2 retention within the bone defect and BMP-2 release into surrounding soft tissues. HMP delivery of BMP-2 may provide a method of tuning BMP-2 release in vivo that can be further investigated to improve current methods of bone regeneration.
View Publication
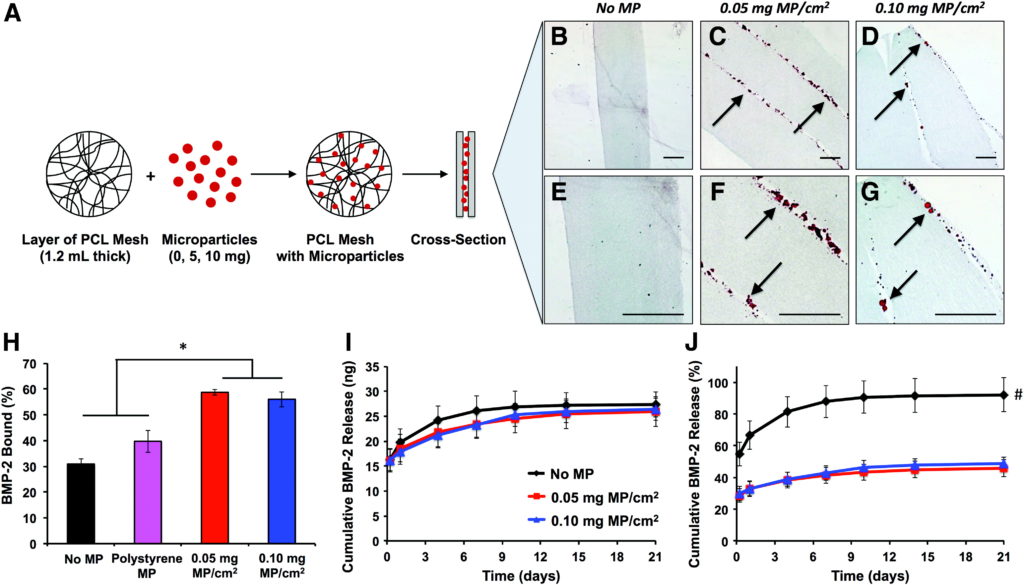
Tissue engineering strategies involving the in vivo delivery of recombinant growth factors are often limited by the inability of biomaterials to spatially control diffusion of the delivered protein within the site of interest. The poor spatiotemporal control provided by porous collagen sponges, which are used for the clinical delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) for bone regeneration, has necessitated the use of supraphysiological protein doses, leading to inflammation and heterotopic ossification. This study describes a novel tissue engineering strategy to spatially control rapid BMP-2 diffusion from collagen sponges in vivo by creating a high affinity BMP-2 sink around the collagen sponge. We designed an electrospun poly-e-caprolactone nanofiber mesh containing physically entrapped heparin microparticles, which have been previously demonstrated to bind and retain large amounts of BMP-2. Nanofiber meshes containing 0.05 and 0.10 mg of microparticles/cm2 demonstrated increased BMP-2 binding and decreased BMP-2 release in vitro compared with meshes without microparticles. However, when microparticle-containing meshes were used in vivo to limit the diffusion of BMP-2 delivered by using collagen sponges in a rat femoral defect, no differences in heterotopic ossification or biomechanical properties were observed. Further investigation revealed that, although BMP-2 binding to heparin microparticles was rapid, the presence of serum components attenuated microparticle-BMP-2 binding and increased BMP-2 release in vitro. These observations provide a plausible explanation for the results observed in vivo and suggest that competitive protein binding in vivo may hinder the ability of affinity-based biomaterials to modulate growth factor delivery.
Press Release: How to Engineer a Stronger Immune System
View Publication
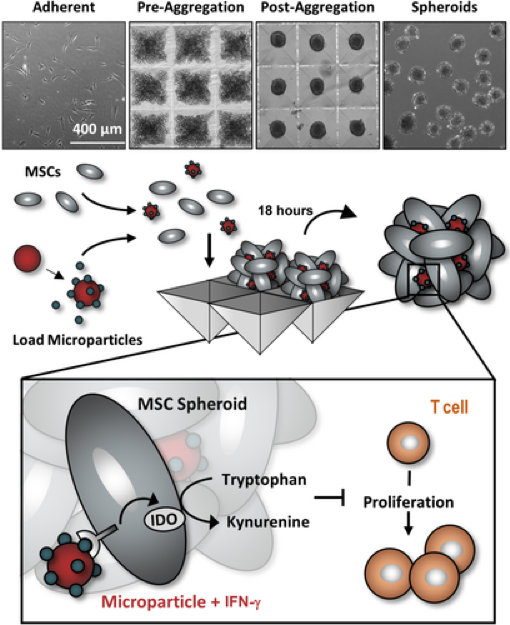
The immunomodulatory activity of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) to suppress innate and adaptive immune responses offers a potent cell therapy for modulating inflammation and promoting tissue regeneration. However, the inflammatory cytokine milieu plays a critical role in stimulating MSC immunomodulatory activity. In particular, interferon-g (IFN-g)-induced expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is primarily responsible for MSC suppression of T-cell proliferation and activation. Although pretreatment with IFN-g is commonly used to prime MSCs for immunomodulatory activity prior to transplantation, the transient effects of pretreatment may limit the potential of MSCs to potently modulate immune responses. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate whether microparticle-mediated presentation of bioactive IFN-g within three-dimensional spheroidal MSC aggregates could precisely regulate and induce sustained immunomodulatory activity. Delivery of IFN-g via heparin-microparticles within MSC aggregates induced sustained IDO expression during 1 week of culture, whereas IDO expression by IFN-g-pretreated MSC spheroids rapidly decreased during 2 days. Furthermore, sustained IDO expression induced by IFN-g-loaded microparticles resulted in an increased and sustained suppression of T-cell activation and proliferation in MSC cocultures with CD3/CD28-activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The increased suppression of T cells by MSC spheroids containing IFN-g-loaded microparticles was dependent on induction of IDO and supported by affecting monocyte secretion from pro- to anti-inflammatory cytokines. Altogether, microparticle delivery of IFN-g within MSC spheroids provides a potent means of enhancing and sustaining immunomodulatory activity to control MSC immunomodulation after transplantation and thereby improve the efficacy of MSC-based therapies aimed at treating inflammatory and immune diseases.
2016
View Publication
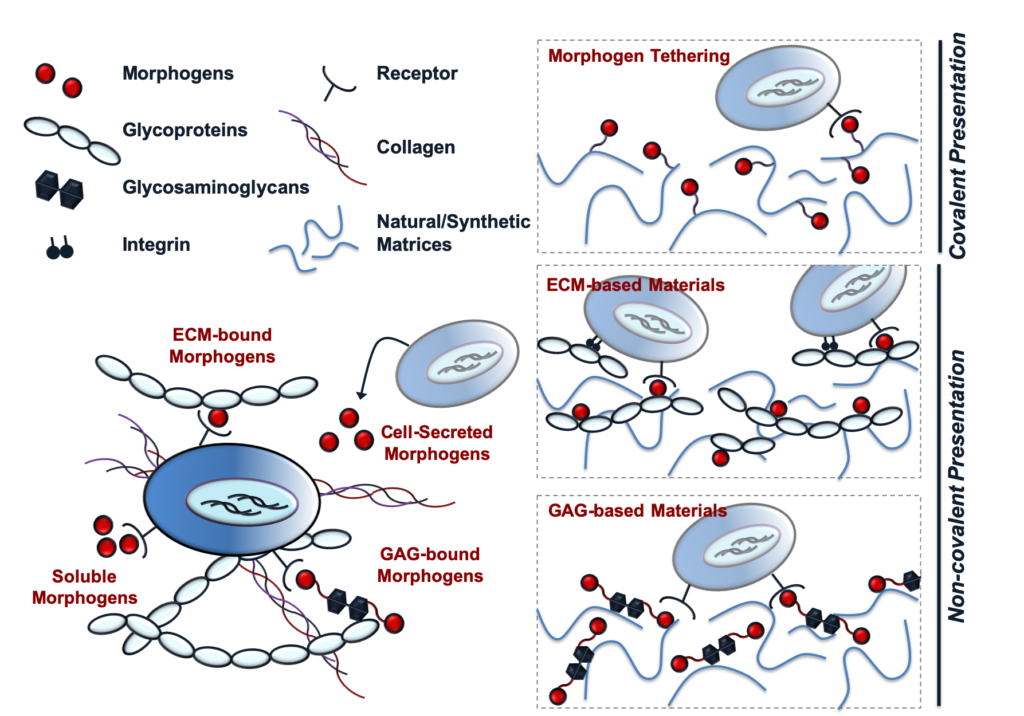
Protein sequestration plays an essential role in maintaining stem cell populations in the native stem cell niche. Both pluripotent and adult stem cells require the sustained presentation of numerous bioactive growth factors and other soluble cues to potentiate cell fate decisions and morphogenic events. Consequently, methods of natural protein sequestration employed by the stem cell niche present attractive strategies for developing novel protein delivery vehicles and engineering biomimetic stem cell microenvironments that enhance morphogen bioactivity. In this review, we will explore the role of protein sequestration in the native stem cell niche and how it has inspired the design of several classes of materials that exploit natural protein sequestration to effectively maintain stem cell populations and direct stem cell fate. We will also highlight several recent developments in protein sequestering biomaterials, in which material strategies to sequester complex mixtures of endogenously secreted proteins are also being investigated.
2014
Press Release: Engineering a Better Way to Rebuild Bone Inside the Body
View Publication
Biomaterials capable of providing localized and sustained presentation of bioactive proteins are critical for effective therapeutic growth factor delivery. However, current biomaterial delivery vehicles commonly suffer from limitations that can result in low retention of growth factors at the site of interest or adversely affect growth factor bioactivity. Heparin, a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is an attractive growth factor delivery vehicle due to its ability to reversibly bind positively charged proteins, provide sustained delivery, and maintain protein bioactivity. This study describes the fabrication and characterization of heparin methacrylamide (HMAm) microparticles for recombinant growth factor delivery. HMAm microparticles were shown to efficiently bind several heparin-binding growth factors (e.g. bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2)), including a wide range of BMP-2 concentrations that exceeds the maximum binding capacity of other common growth factor delivery vehicles, such as gelatin. BMP-2bioactivity was assessed on the basis of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity induced in skeletal myoblasts (C2C12). Microparticles loaded with BMP-2 stimulated comparable C2C12 ALP activity to soluble BMP-2 treatment, indicating that BMP-2-loaded microparticles retain bioactivity and potently elicit afunctional cell response. In summary, our results suggest that heparin microparticles stably retain large amounts of bioactive BMP-2 for prolonged periods of time, and that presentation of BMP-2 via heparin microparticles can elicit cell responses comparable to soluble BMP-2 treatment. Consequently, heparin microparticles present an effective method of delivering and spatially retaining growth factors that could be used in a variety of systems to enable directed induction of cell fates and tissue regeneration.